Table of Contents
- What is Maternity Leave?
- Maternity Leave Policy in India
- Who is Eligible to Apply for Maternity Leave?
- Maternity Leave Rules in India
- Benefits of Maternity Leave in India
- Legal Framework: The Maternity Benefit Act, 1961 & 2017 Amendment
- Maternity Leave Duration in India (Table)
- Difficulties Faced by Female Employees
- Legal References for Maternity Leave Policy in India
Motherhood has to be a peaceful journey for every woman out there. It is not only about bringing new life into the world but also providing mothers with the space, time and dignity they deserve during the pregnancy phase. Creating a good maternity leave policy will be the fundamental aspect in supporting, respecting and protecting before and after delivery.
What is Maternity Leave?
Maternity leave is a legally protected absence from work granted to female employees during pregnancy and after childbirth. It allows them to recover, bond with their newborn, and return to work without the fear of losing their job or income.
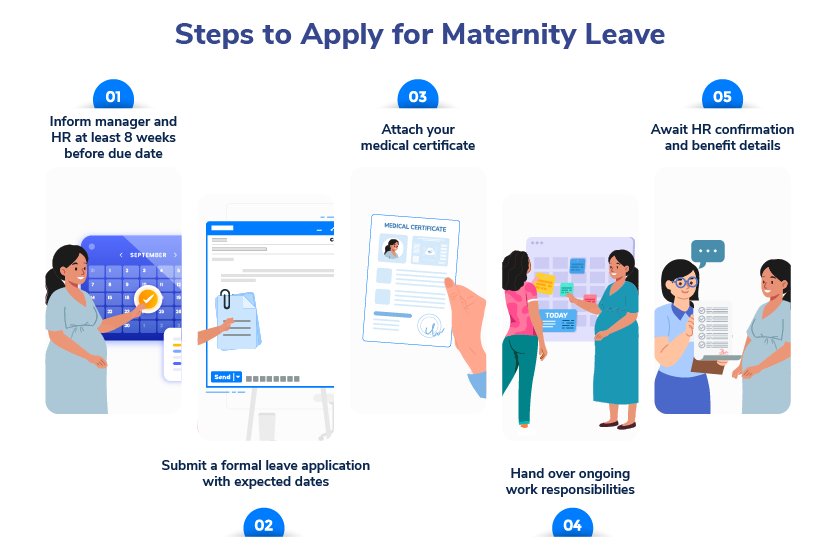
Maternity Leave Policy in India
In India, maternity leave is governed by the Maternity Benefit Act, which has undergone several amendments to stay relevant to evolving work cultures and societal needs. The policy not only protects a woman’s employment during maternity but also ensures she receives certain benefits during this period.
Who is Eligible to Apply for Maternity Leave?
To apply for maternity leave in India, the female employee must meet the following criteria:
- She should be employed in an organisation with 10 or more employees.
- She must have worked for at least 80 days in the 12 months preceding her expected delivery date.
- Eligibility applies to all women, including those on contract (as long as the minimum workdays are met).
- Applicable to private/public sector, factories, mines, shops, and other establishments.
Maternity Leave Rules in India
Both employers and employees should understand the rules of maternity leave to ensure a smooth process in the organisation.
Leave Timing
Staff can avail 8 weeks before the delivery date and remaining post-delivery date. The leave timing is flexible and it depends on the staff’s needs. If a female employee requires more leaves post-delivery, it can be adjusted accordingly.
Medical Certificate
- A doctor’s certificate confirming the pregnancy and expected delivery date is important to proceed with the maternity leave.
Documents Required
- Doctor’s certificate
- Ultrasound report
- Maternity leave form
- Employee ID / Proof of Employment ac
Employee Compliance
- From the employee’s end, they should inform employers about the leave requirements in prior.
- The internal leave policy should be followed to stay compliant.
Priya Sharma, a Senior Marketing Executive at a IT firm, applied for maternity leave in her 7th month of pregnancy. She informed her HR department two months in advance, submitted her medical certificate, and opted for 8 weeks before and 18 weeks after delivery. The company not only approved her leave under the Maternity Benefit Act but also arranged flexible work-from-home options for her return phase. This helped her transition smoothly back into work without compromising on her health or bonding time with her baby.
Benefits of Maternity Leave in India
Maternity leave is a fundamental right of every woman. Here are the benefits:
- Paid Leave: Full pay for eligible days as per The Maternity Benefit Act, 1961
- Job Protection: Assurance to offer the same or equivalent position post-maternity
- Safety: Time to recover from childbirth physically, mentally and emotionally
- Work-Life Balance: Promotes a smooth transition into motherhood
- Support for New-Age Mothers: Now includes adoption, surrogacy, and miscarriage-related leave
Legal Framework: Maternity Benefit Act, 1961 and Amendment 2017
- The Maternity Benefit Act, 1961, was India’s foundational law to protect the employment of women during maternity.
- The 2017 Amendment brought in significant updates:
- Female employees get additional leave from 12 to 26 weeks for the first two kids.
- The latest amendment also allows leave for adoptive and commissioning mothers as well.
- Crèche facilities are mandatory for establishments with 50+ employees.
- Work-from-home options available post-leave if applicable.
Maternity Leave Duration in India
| First Child | 26 weeks |
| Second Child | 26 weeks |
| Third Child Onwards | 12 weeks |
| Adoption (child <3 months) | 12 weeks (from adoption date) |
| Commissioning Mother (surrogacy) | 12 weeks |
| Miscarriage | 6 weeks |
| Tubectomy (after sterilisation surgery) | 2 weeks |
| Prenatal Leave | Limit Up to 8 weeks before delivery |
Difficulties Faced by Female Employees
Though the maternity leave policy is provided, implementing it in the real world is still a hurdle.
- Lack of awareness about rights among women employees
- Workplace bias or fear of being replaced during the absence
- Lack of flexibility post-return (e.g., no WFH options)
- Crèche non-compliance by smaller organisations
- Cultural stigma, especially in male-dominated industries
Official Legal References for Maternity Leave Policy in India
- Definition of Maternity Leave : As per Section 5(2) of the Maternity Benefit Act, 1961 (Official Text), every woman shall be entitled to maternity benefit at the rate of the average daily wage for the period of her actual absence.
- Eligibility Criteria : Section 5(2) clearly states that to be eligible, a woman must have worked for at least 80 days in the 12 months immediately preceding her expected delivery date.
- Leave Duration : Under the Maternity Benefit (Amendment) Act, 2017, the leave entitlement was increased from 12 weeks to 26 weeks for the first two surviving children (Section 5(3), Official Gazette).
- Adoptive & Commissioning Mothers: As per Section 5(4), adoptive mothers (with a child below 3 months) and commissioning mothers are entitled to 12 weeks of leave from the date the child is handed over.
- Crèche Facility Requirement: Section 11A, inserted by the 2017 Amendment, mandates that every establishment with 50 or more employees must provide a crèche facility, with four visits per day allowed to the mother.
- Work From Home Option: Section 5(5) allows employers to permit work-from-home arrangements after maternity leave, depending on the nature of work and mutual agreement.
Wrapping Up
Maternity is a temporary pause in a woman’s career. It’s time employers not only comply with laws but also embrace the human side of HR. A respectful and smooth maternity experience isn’t just about ticking boxes but also honouring life, health, and motherhood.
FAQs
1. Can maternity leave be extended beyond 26 weeks?
Only under exceptional medical circumstances or company discretion. However, such leave is usually unpaid unless otherwise specified by employer policy.
2. Can women take maternity leave for a third child?
Yes, but the duration is 12 weeks, only 6 before and 6 after delivery.
3. What is the maternity benefit for contract employees?
If the employee meets the 80-day work rule and is in an eligible establishment, she is entitled to maternity leave and pay.
4. Are women eligible for maternity leave during probation?
Yes, provided she meets the 80-day rule within the 12 months preceding her expected delivery date.
5. Do adoptive mothers receive maternity leave?
Yes, if the adopted child is less than 3 months old. They are entitled to 12 weeks of leave from the adoption date.
6. Is it mandatory for companies to offer work-from-home after maternity leave?
Not mandatory, but the 2017 amendment encourages it based on mutual agreement between employer and employee.
7. Can maternity leave be combined with other leaves?
Yes, many companies allow combining sick leave or paid leave after maternity leave, but it depends on the company’s policy.

